GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
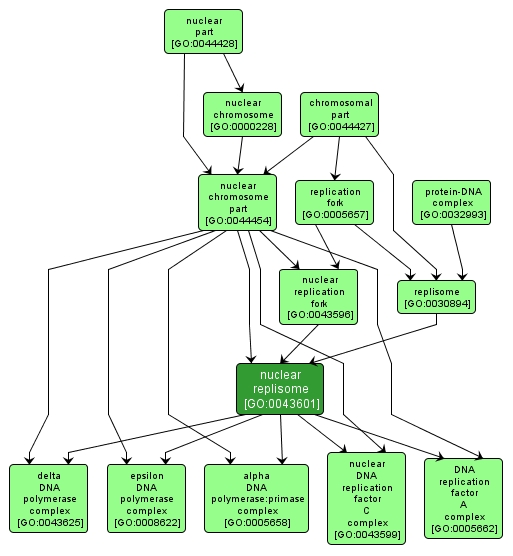
nuclear replisome |
| Acc: |
GO:0043601 |
| Aspect: |
Cellular Component |
| Desc: |
A multi-component enzymatic machine at the nuclear replication fork, which mediates DNA replication. Includes DNA primase, one or more DNA polymerases, DNA helicases, and other proteins. |
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|