GO TERM SUMMARY
|
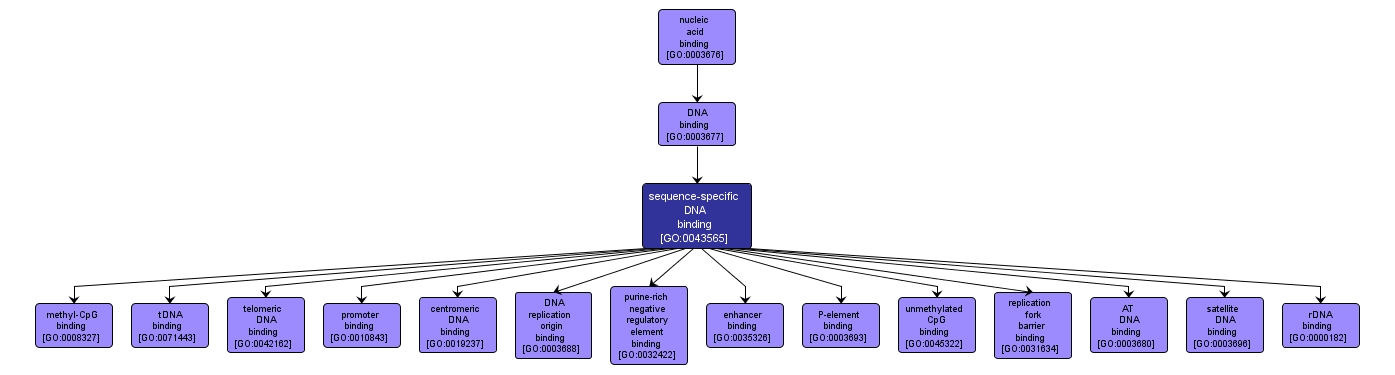
| Name: |
sequence-specific DNA binding |
| Acc: |
GO:0043565 |
| Aspect: |
Molecular Function |
| Desc: |
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with DNA of a specific nucleotide composition, e.g. GC-rich DNA binding, or with a specific sequence motif or type of DNA e.g. promotor binding or rDNA binding. |
Synonyms:
- sequence specific DNA binding
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|