GO TERM SUMMARY
|
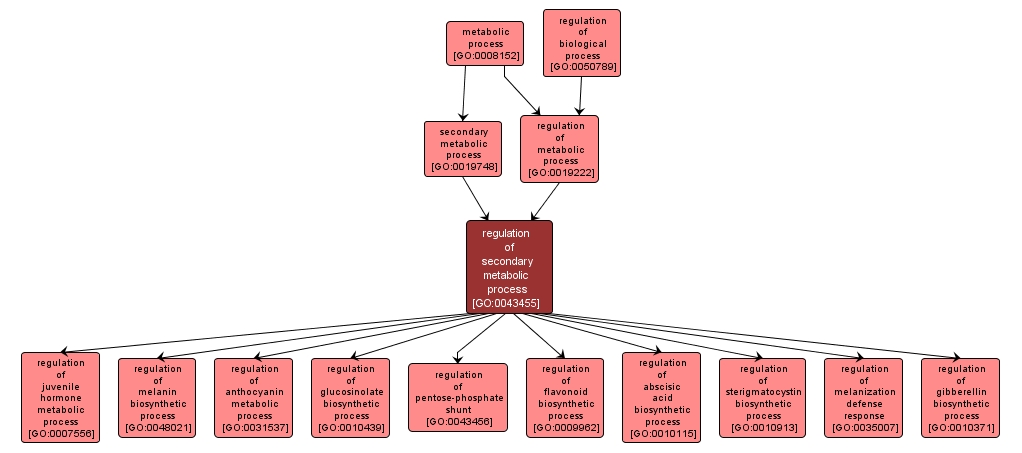
| Name: |
regulation of secondary metabolic process |
| Acc: |
GO:0043455 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of secondary metabolism, the chemical reactions and pathways involving compounds that are not necessarily required for growth and maintenance of cells, and are often unique to a taxon. |
Synonyms:
- regulation of secondary metabolism
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|