GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
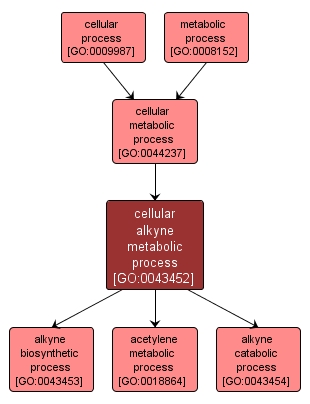
cellular alkyne metabolic process |
| Acc: |
GO:0043452 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
The chemical reactions and pathways involving an alkyne, any cyclic branched or unbranched hydrocarbon having a carbon-carbon triple bond and the general formula CnH2n-2, as carried out by individual cells. |
| Synonyms:
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|