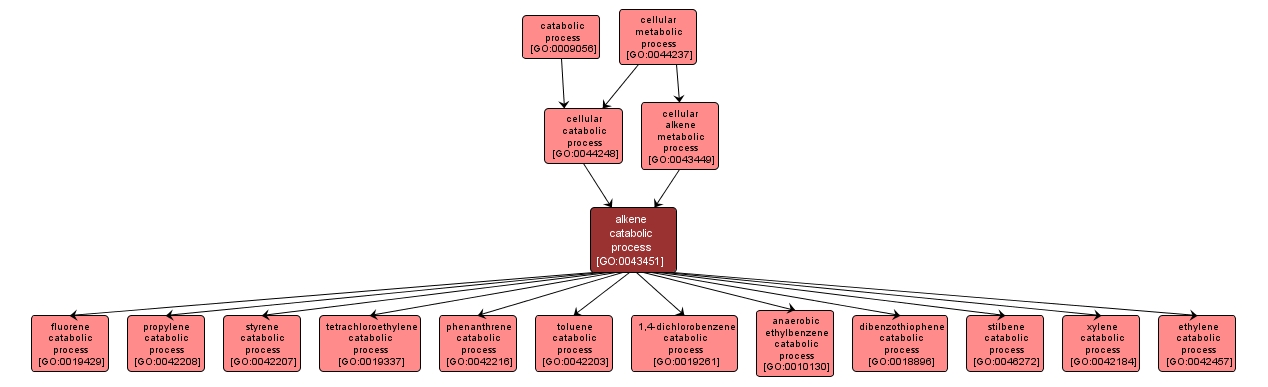
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
alkene catabolic process |
| Acc: |
GO:0043451 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of an alkene, any cyclic branched or unbranched hydrocarbon having one carbon-carbon double bond and the general formula CnH2n. |
Synonyms:
- alkene breakdown
- alkene catabolism
- alkene degradation
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|