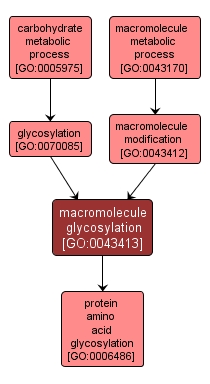
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
macromolecule glycosylation |
| Acc: |
GO:0043413 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
The covalent attachment of a glycosyl residue to one or more monomeric units in a polypeptide, polynucleotide, polysaccharide, or other biological macromolecule. |
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|