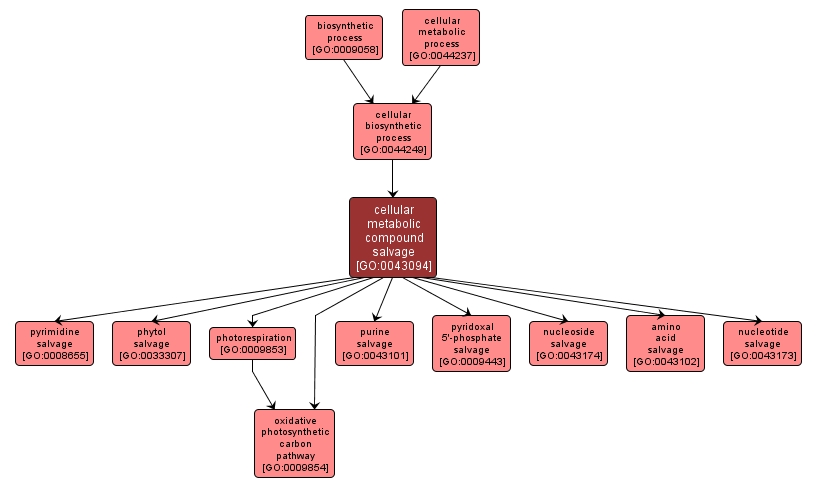
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
cellular metabolic compound salvage |
| Acc: |
GO:0043094 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
Any process which produces a useful metabolic compound from derivatives of it without de novo synthesis, as carried out by individual cells. |
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|