GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
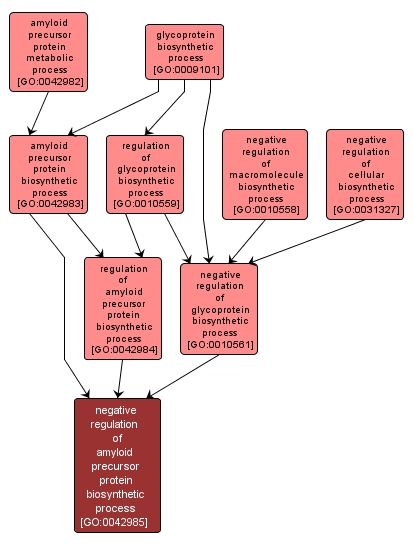
negative regulation of amyloid precursor protein biosynthetic process |
| Acc: |
GO:0042985 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of amyloid precursor protein (APP), the precursor of beta-amyloid. |
Synonyms:
- negative regulation of APP biosynthesis
- negative regulation of amyloid precursor protein anabolism
- down-regulation of amyloid precursor protein biosynthetic process
- downregulation of amyloid precursor protein biosynthetic process
- negative regulation of APP biosynthetic process
- inhibition of amyloid precursor protein biosynthetic process
- negative regulation of amyloid precursor protein synthesis
- down regulation of amyloid precursor protein biosynthetic process
- negative regulation of amyloid precursor protein formation
- negative regulation of amyloid precursor protein biosynthesis
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|