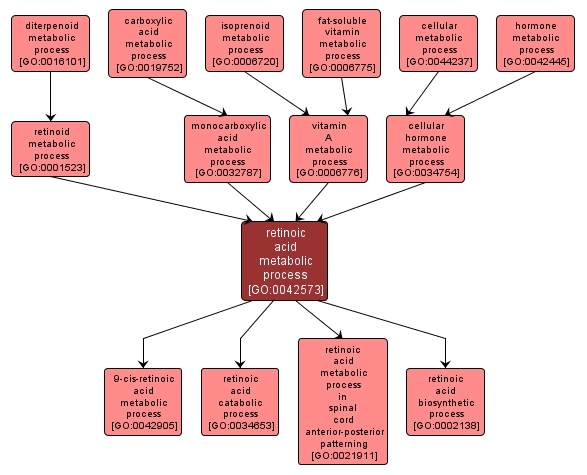
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
retinoic acid metabolic process |
| Acc: |
GO:0042573 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
The chemical reactions and pathways involving retinoic acid, one of the three components that makes up vitamin A. |
Synonyms:
- retinoic acid metabolism
- vitamin A1 acid metabolism
- vitamin A1 acid metabolic process
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|