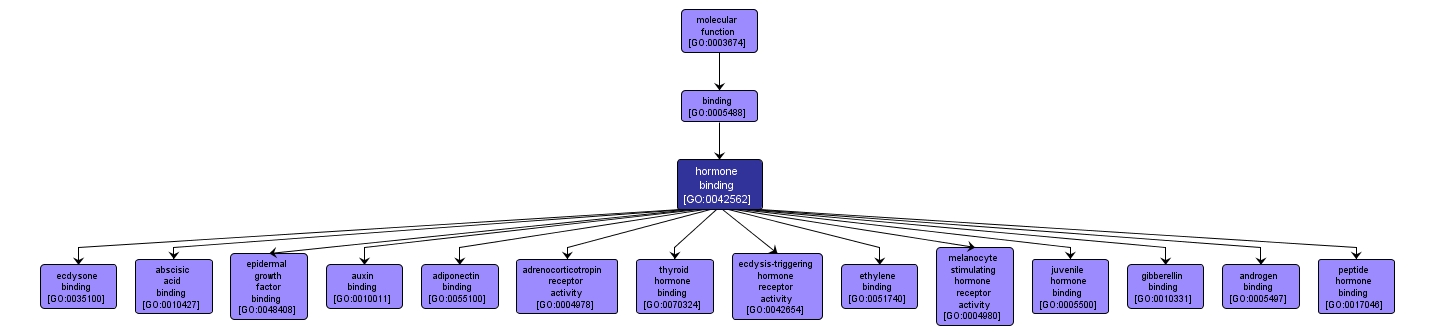
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
hormone binding |
| Acc: |
GO:0042562 |
| Aspect: |
Molecular Function |
| Desc: |
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with any hormone, naturally occurring substances secreted by specialized cells that affect the metabolism or behavior of other cells possessing functional receptors for the hormone. |
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|