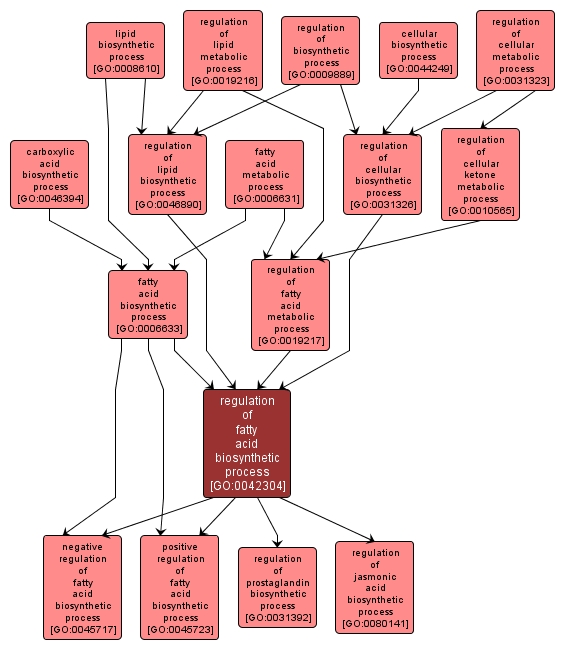
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
regulation of fatty acid biosynthetic process |
| Acc: |
GO:0042304 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of fatty acids, any of the aliphatic monocarboxylic acids that can be liberated by hydrolysis from naturally occurring fats and oils. |
Synonyms:
- regulation of fatty acid biosynthesis
- regulation of fatty acid synthesis
- regulation of fatty acid anabolism
- regulation of fatty acid formation
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|