GO TERM SUMMARY
|
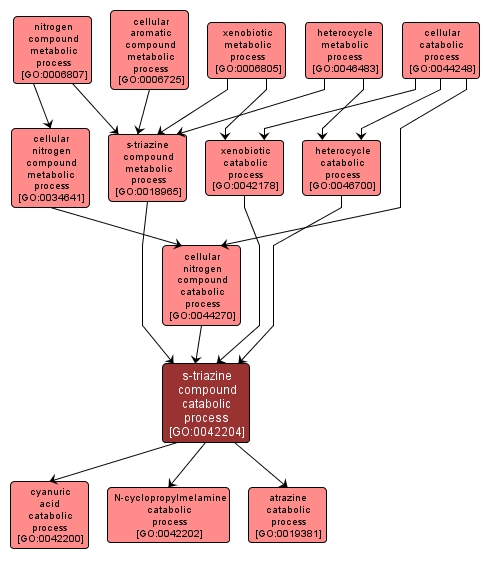
| Name: |
s-triazine compound catabolic process |
| Acc: |
GO:0042204 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of any s-triazine compound. These compounds include many pesticides of widespread use in agriculture, and are characterized by a symmetrical hexameric ring consisting of alternating carbon and nitrogen atoms. |
Synonyms:
- s-triazine compound degradation
- s-triazine compound breakdown
- s-triazine compound catabolism
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|