| Desc: |
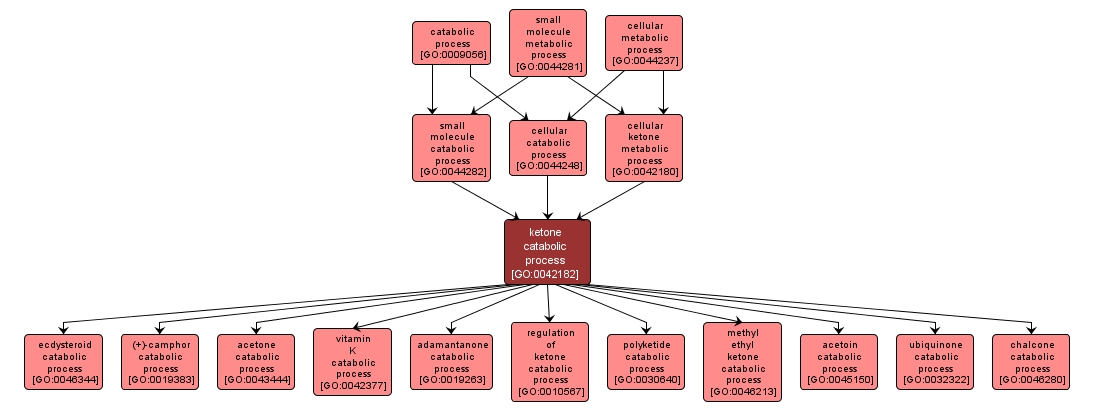
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of ketones, a class of organic compounds that contain the carbonyl group, CO, and in which the carbonyl group is bonded only to carbon atoms. The general formula for a ketone is RCOR, where R and R are alkyl or aryl groups. |