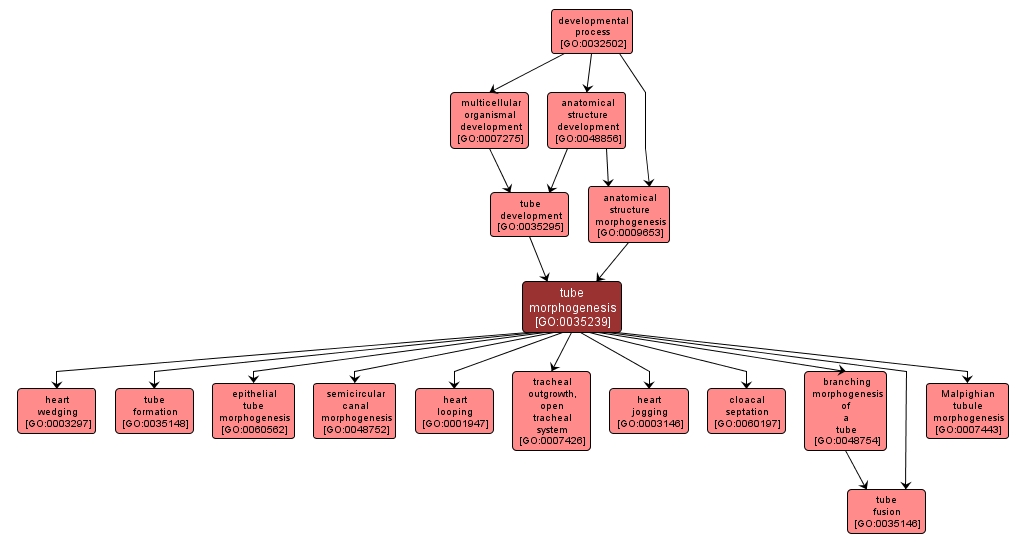
| Desc: |
The process by which the anatomical structures of a tube are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form. Epithelial and endothelial tubes transport gases, liquids and cells from one site to another and form the basic structure of many organs and tissues, with tube shape and organization varying from the single-celled excretory organ in Caenorhabditis elegans to the branching trees of the mammalian kidney and insect tracheal system. |