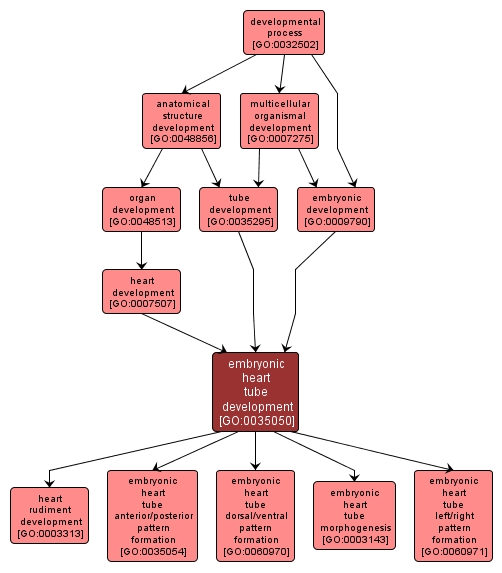
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
embryonic heart tube development |
| Acc: |
GO:0035050 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the embryonic heart tube over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The heart tube forms as the heart rudiment from the heart field. |
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|