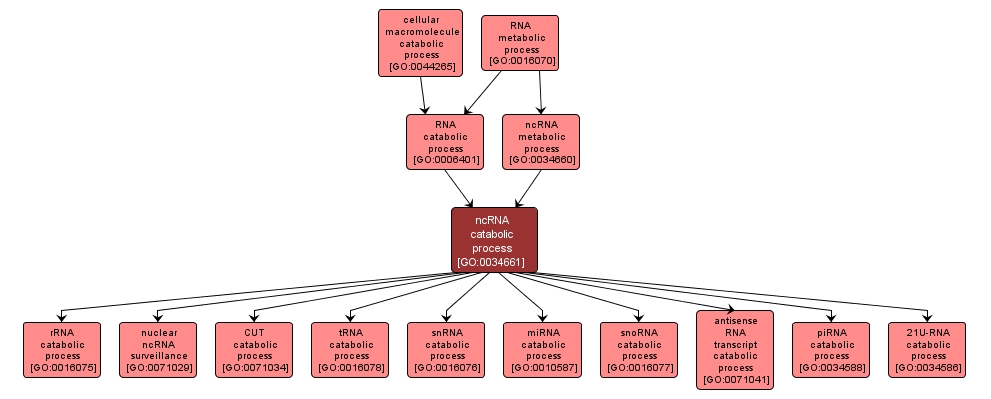
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
ncRNA catabolic process |
| Acc: |
GO:0034661 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of non-coding RNA transcripts (ncRNAs). Includes the breakdown of cryptic unstable transcripts (CUTs). |
Synonyms:
- ncRNA degradation
- ncRNA breakdown
- ncRNA catabolism
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|