| Desc: |
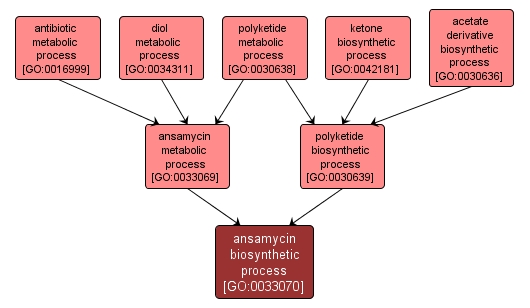
The chemical reactions and pathways leading to the formation of ansamycins, any of a group of complex macrolactam compounds characterized by a cyclic structure in which an aliphatic ansa chain forms a bridge between two non-adjacent positions of a cyclic p-system; many exhibit antibacterial, antifungal or antitumor activity. |