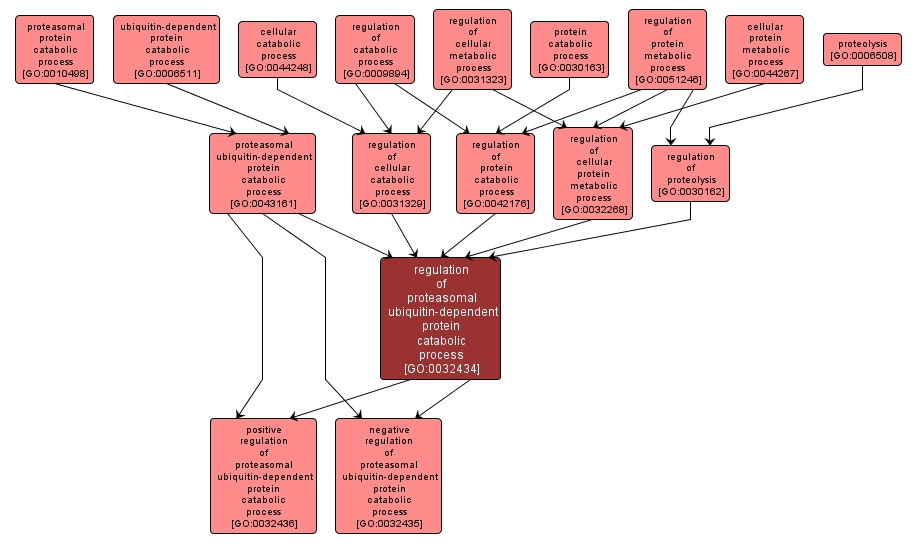
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
regulation of proteasomal ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process |
| Acc: |
GO:0032434 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the breakdown of a protein or peptide by hydrolysis of its peptide bonds, initiated by the covalent attachment of ubiquitin, and mediated by the proteasome. |
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|