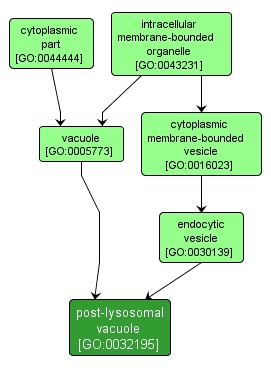
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
post-lysosomal vacuole |
| Acc: |
GO:0032195 |
| Aspect: |
Cellular Component |
| Desc: |
A membrane-bounded intracellular vesicle formed late in the endocytic pathway when the pH in the vacuole becomes neutral prior to exocytosis. |
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|