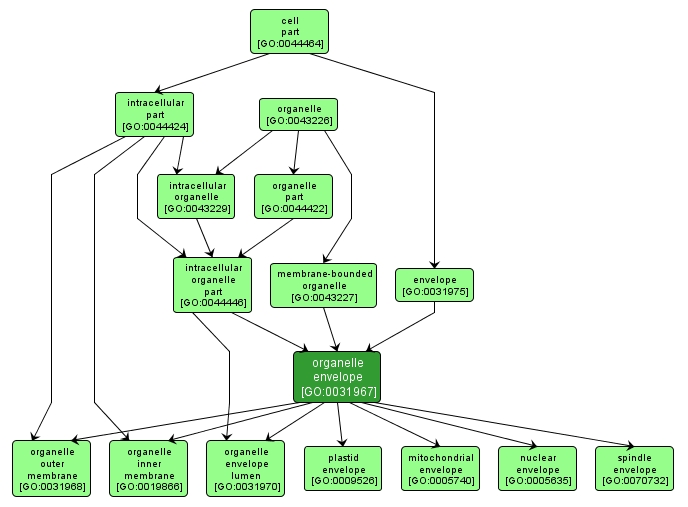
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
organelle envelope |
| Acc: |
GO:0031967 |
| Aspect: |
Cellular Component |
| Desc: |
A double membrane structure enclosing an organelle, including two lipid bilayers and the region between them. In some cases, an organelle envelope may have more than two membranes. |
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|