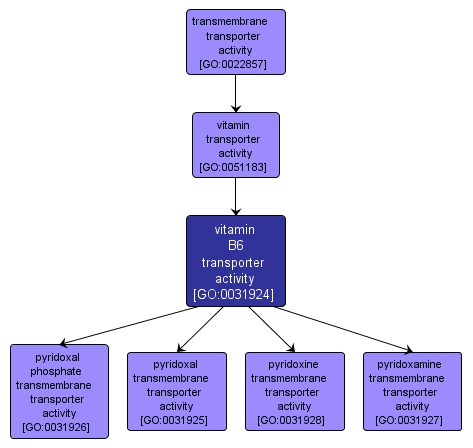
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
vitamin B6 transporter activity |
| Acc: |
GO:0031924 |
| Aspect: |
Molecular Function |
| Desc: |
Enables the directed movement of any of the vitamin B6 compounds -- pyridoxal, pyridoxamine and pyridoxine and the active form, pyridoxal phosphate -- into, out of, within or between cells. |
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|