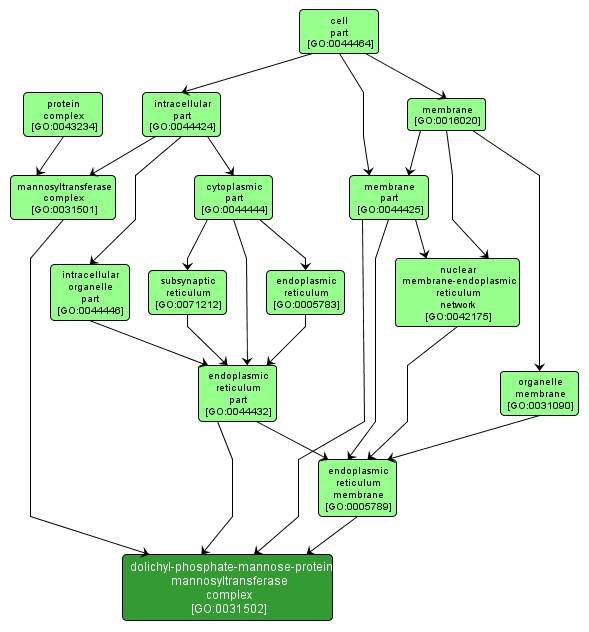
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
dolichyl-phosphate-mannose-protein mannosyltransferase complex |
| Acc: |
GO:0031502 |
| Aspect: |
Cellular Component |
| Desc: |
A complex that possesses dolichyl-phosphate-mannose-protein mannosyltransferase activity; usually includes members of the PMT1 and PMT2 protein subfamilies. |
Synonyms:
- protein O-mannosyltransferase complex
- PMT family mannosyltransferase complex
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|