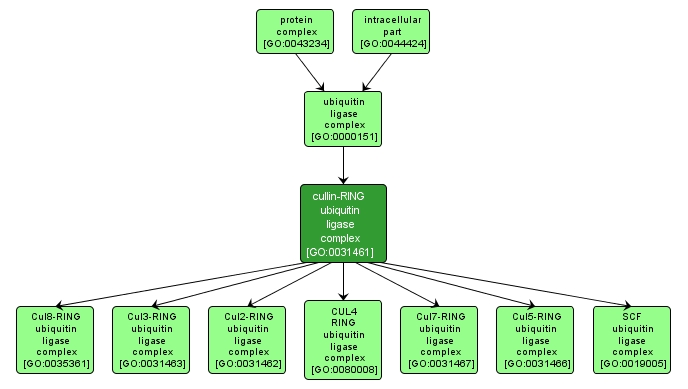
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
cullin-RING ubiquitin ligase complex |
| Acc: |
GO:0031461 |
| Aspect: |
Cellular Component |
| Desc: |
Any ubiquitin ligase complex in which the catalytic core consists of a member of the cullin family and a RING domain protein; the core is associated with one or more additional proteins that confer substrate specificity. |
Synonyms:
- CRL complex
- cullin-RING ligase
- cullin complex
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|