| Desc: |
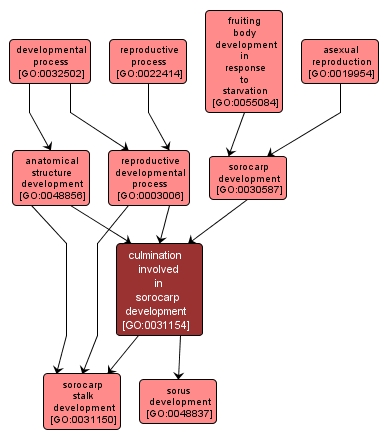
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the culminant over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Culmination begins with a morphogenetic change of the finger-like or migratory slug giving rise to an organized structure containing a stalk and a sorus. This process is the final stage of sorocarp development. |