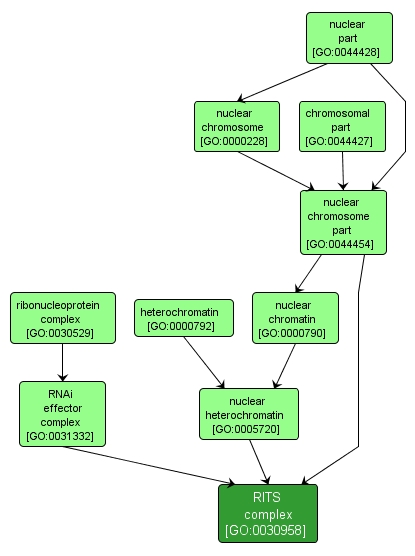
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
RITS complex |
| Acc: |
GO:0030958 |
| Aspect: |
Cellular Component |
| Desc: |
A protein complex required for heterochromatin assembly; contains an Argonaute homolog, a chromodomain protein, and at least one additional protein; named for RNA-induced initiation of transcriptional gene silencing. |
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|