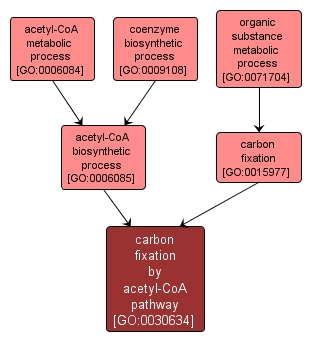
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
carbon fixation by acetyl-CoA pathway |
| Acc: |
GO:0030634 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
A pathway of carbon dioxide fixation in which one molecule of acetyl-CoA is completely synthesized from two molecules of carbon dioxide (CO2). |
| Synonyms:
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|