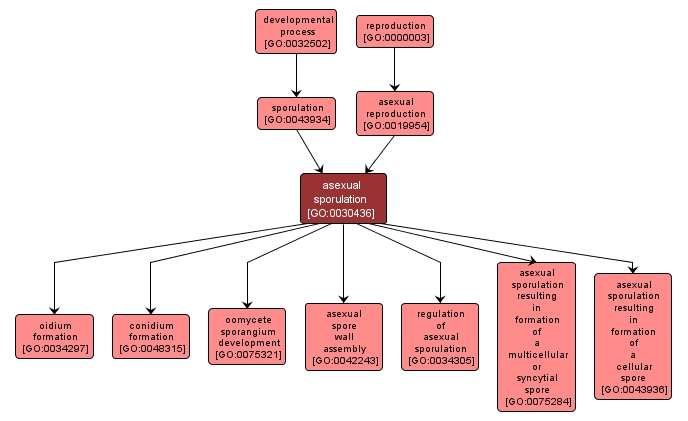
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
asexual sporulation |
| Acc: |
GO:0030436 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
The formation of spores derived from the products of mitosis. Examples of this process are found in Bacterial species. |
Synonyms:
- asexual spore formation
- mitotic sporulation
- mitotic spore formation
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|