| Desc: |
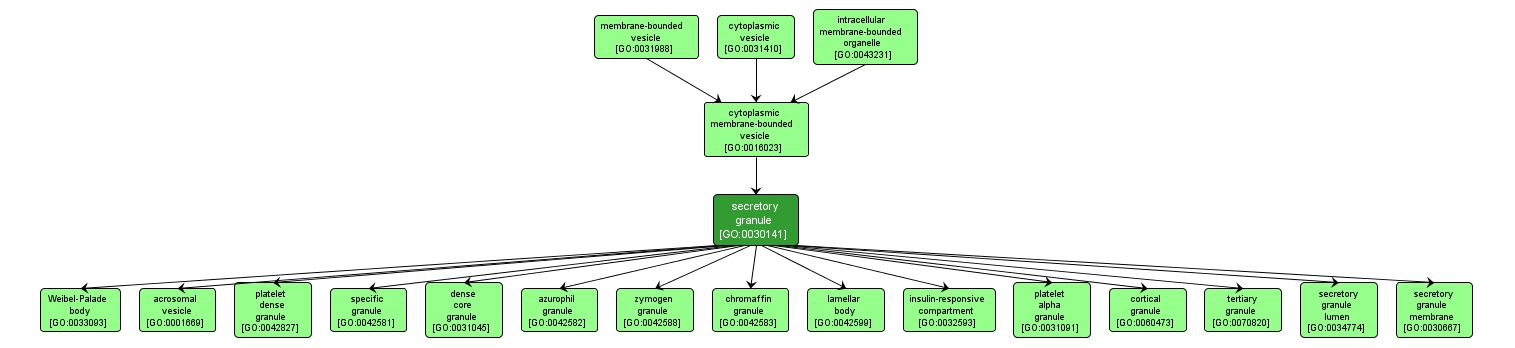
A small subcellular vesicle, surrounded by a membrane, that is formed from the Golgi apparatus and contains a highly concentrated protein destined for secretion. Secretory granules move towards the periphery of the cell, their membranes fuse with the cell membrane, and their protein load is exteriorized. Processing of the contained protein may take place in secretory granules. |