| Desc: |
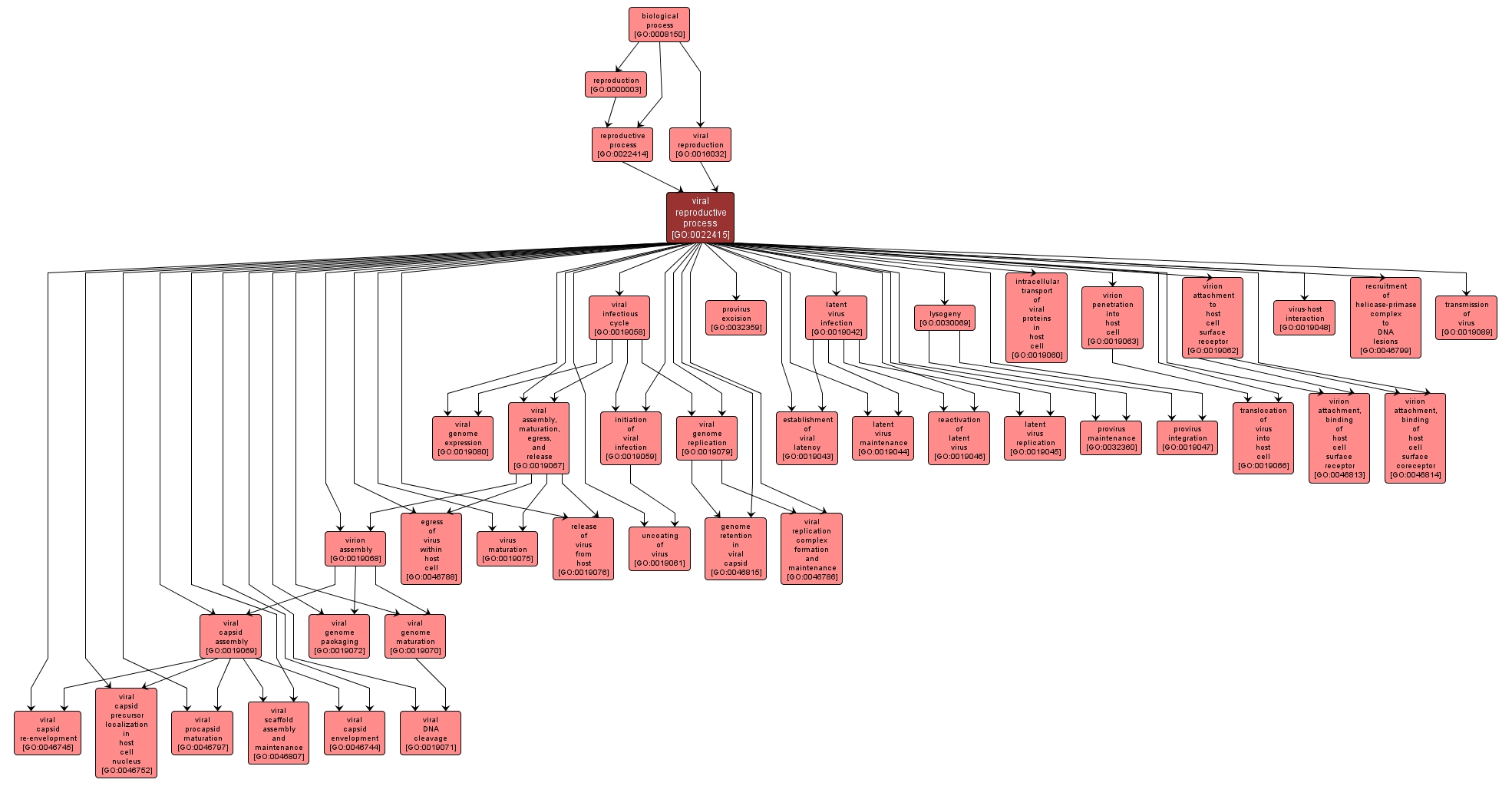
A reproductive process involved in viral reproduction. Usually, this is by infection of a host cell, replication of the viral genome, and assembly of progeny virus particles. In some cases the viral genetic material may integrate into the host genome and only subsequently, under particular circumstances, 'complete' its life cycle. |