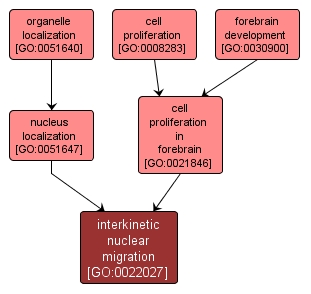
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
interkinetic nuclear migration |
| Acc: |
GO:0022027 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
The movement of the nucleus of the ventricular zone cell between the apical and the basal zone surfaces. Mitosis occurs when the nucleus is near the apical surface, that is, the lumen of the ventricle. |
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|