| Desc: |
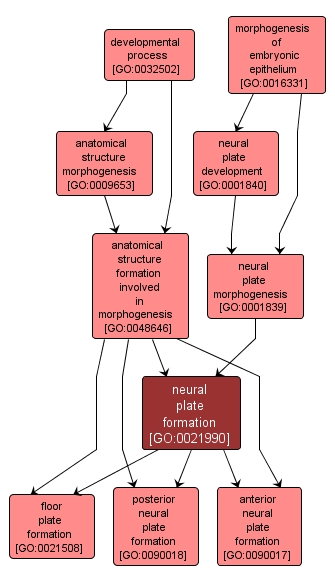
The formation of the flat, thickened layer of ectodermal cells known as the neural plate. The underlying dorsal mesoderm signals the ectodermal cells above it to elongate into columnar neural plate cells. The neural plate subsequently develops into the neural tube, which gives rise to the central nervous system. |