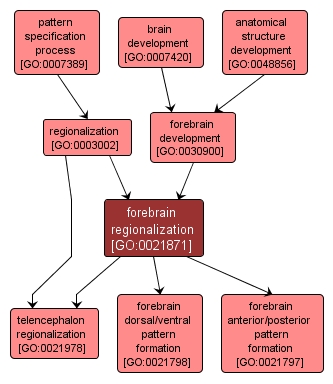
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
forebrain regionalization |
| Acc: |
GO:0021871 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
The regionalization process resulting in the creation of areas within the forebrain that will direct the behavior of cell migration in differentiation as the forebrain develops. |
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|