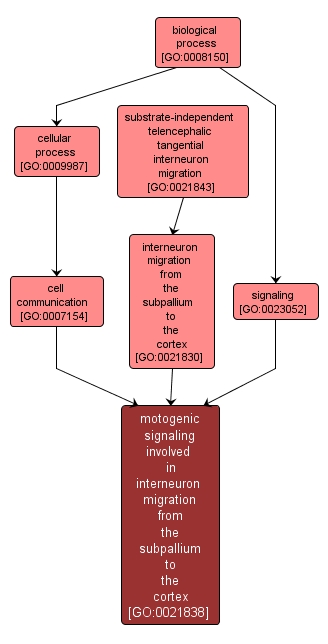
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
motogenic signaling involved in interneuron migration from the subpallium to the cortex |
| Acc: |
GO:0021838 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
The creation and reception of signals that result in the directional movement of interneuron precursors from the subpallium to the cortex. |
Synonyms:
- motogenic signalling involved in interneuron migration from the subpallium to the cortex
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|