| Desc: |
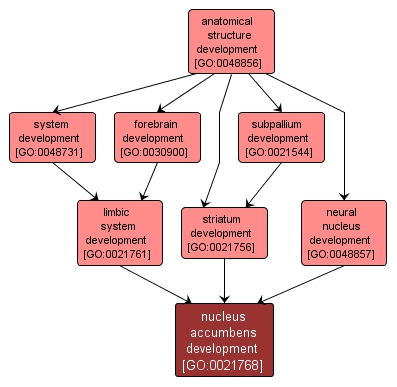
The progression of the nucleus accumbens over time from its initial formation until its mature state. The nucleus accumbens is a collection of pleomorphic cells in the caudal part of the anterior horn of the lateral ventricle, in the region of the olfactory tubercle, lying between the head of the caudate nucleus and the anterior perforated substance. It is part of the ventral striatum, a composite structure considered part of the basal ganglia. |