| Desc: |
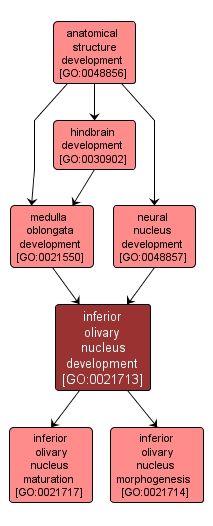
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the inferior olivary nucleus over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The inferior olivary nucleus is a capsule-shaped structure in the ventral medulla located just lateral and dorsal to the medullary pyramids. Neurons in the inferior olivary nucleus are the source of climbing fiber input to the cerebellar cortex; these neurons have been implicated in various functions, such as learning and timing of movements. |