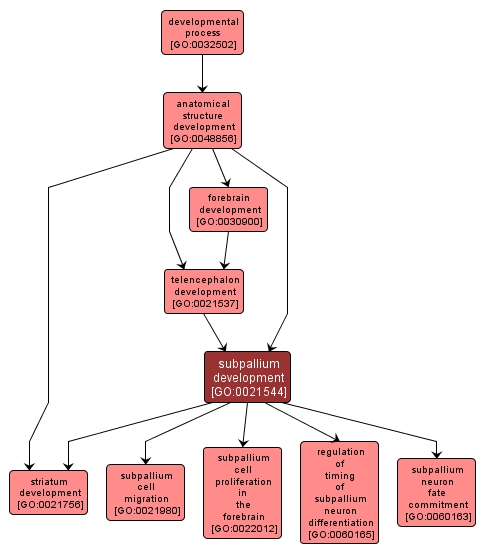
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
subpallium development |
| Acc: |
GO:0021544 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the subpallium over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The subpallium is the base region of the telencephalon. |
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|