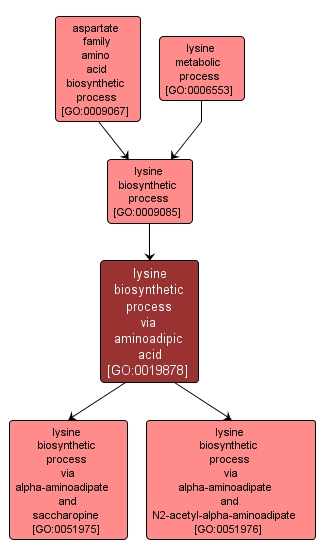
Synonyms:
- lysine biosynthesis, aminoadipic pathway
- lysine biosynthesis, aminoadipic acid pathway
- lysine anabolism via aminoadipic acid
- lysine synthesis via aminoadipic acid
- lysine biosynthetic process, aminoadipic acid pathway
- lysine biosynthetic process, aminoadipic pathway
- lysine formation via aminoadipic acid
|