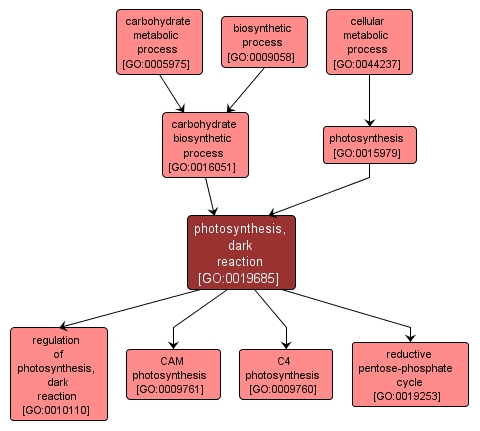
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
photosynthesis, dark reaction |
| Acc: |
GO:0019685 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
A complex cycle of enzyme-mediated reactions which catalyzes the reduction of carbon dioxide to sugar. As well as carbon dioxide the cycle requires reducing power in the form of reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADP) and chemical energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). The reduced NADP (NADPH) and ATP are produced by the 'light' reactions. |
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|