GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
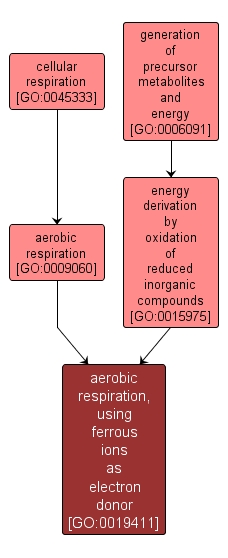
aerobic respiration, using ferrous ions as electron donor |
| Acc: |
GO:0019411 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
The metabolic process by which ferrous ions (Fe2+) are oxidized to ferric ions (Fe3+) to generate energy, coupled to the reduction of carbon dioxide. |
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|