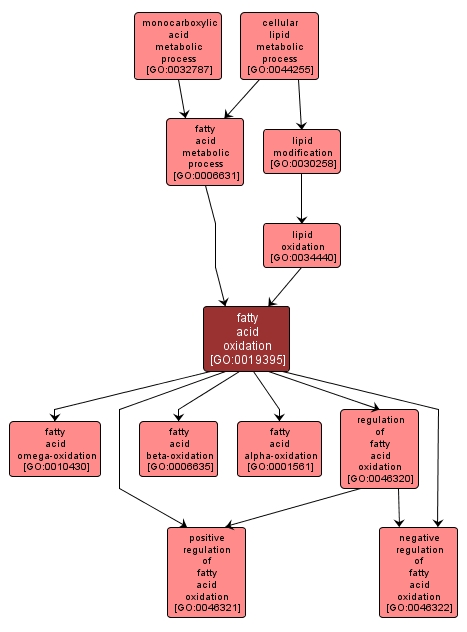
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
fatty acid oxidation |
| Acc: |
GO:0019395 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
The removal of one or more electrons from a fatty acid, with or without the concomitant removal of a proton or protons, by reaction with an electron-accepting substance, by addition of oxygen or by removal of hydrogen. |
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|