| Desc: |
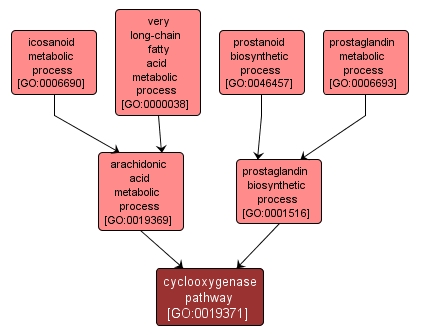
The chemical reactions and pathways by which prostaglandins are formed from arachidonic acid, and in which prostaglandin-endoperoxide synthase (cyclooxygenase) catalyzes the committed step in the conversion of arachidonic acid to the prostaglandin-endoperoxides PGG2 and PGH2. |