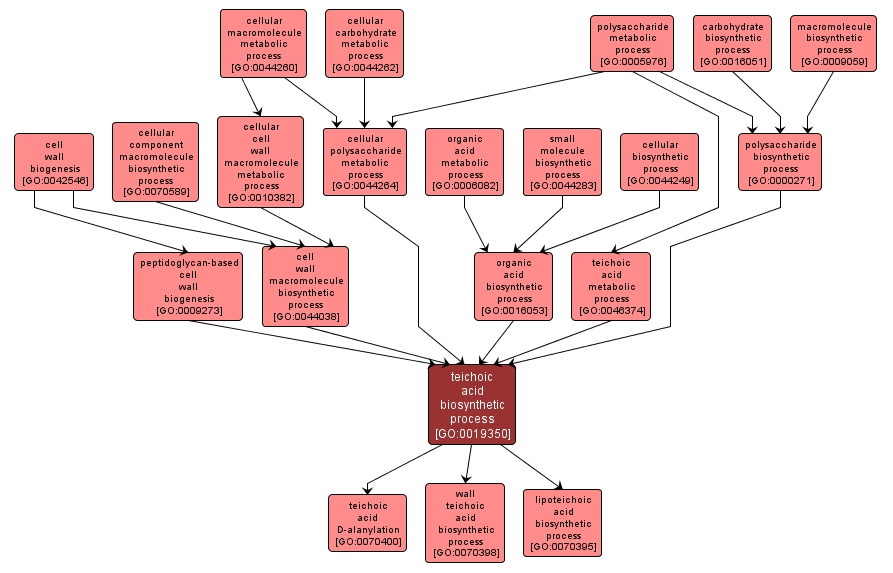
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
teichoic acid biosynthetic process |
| Acc: |
GO:0019350 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of teichoic acid, any polymer occurring in the cell wall, membrane or capsule of Gram-positive bacteria and containing chains of glycerol phosphate or ribitol phosphate residues. |
Synonyms:
- teichoic acid synthesis
- teichoic acid formation
- teichoic acid anabolism
- teichoic acid biosynthesis
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|