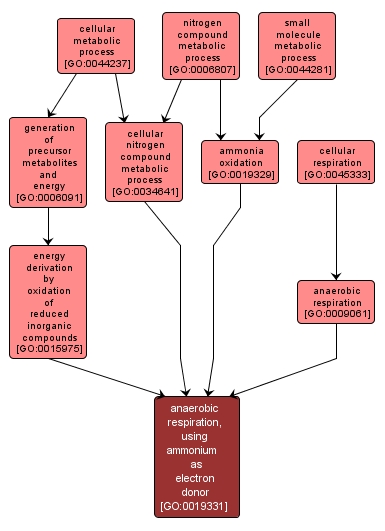
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
anaerobic respiration, using ammonium as electron donor |
| Acc: |
GO:0019331 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
The oxidation of ammonium (NH4) to nitrogen (N2) in the absence of oxygen, using nitrite (NO2) as the electron acceptor. It is suggested that hydroxylamine and ammonium are combined to yield hydrazine, which is subsequently oxidized to N2. |
Synonyms:
- anammox
- anaerobic ammonium oxidation
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|