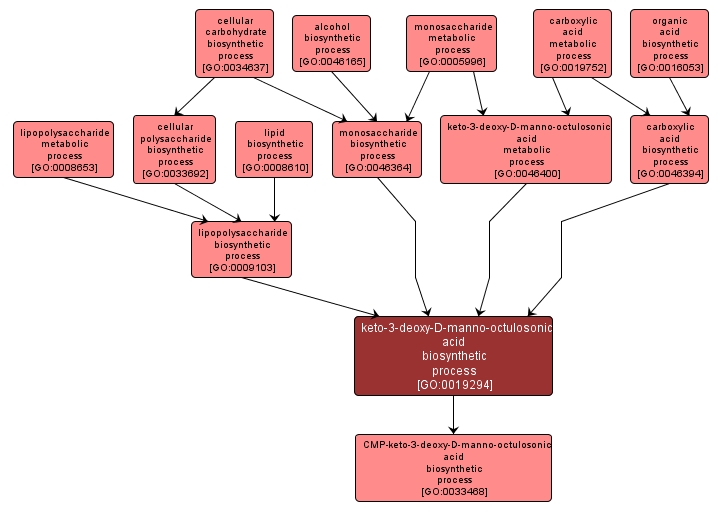
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
keto-3-deoxy-D-manno-octulosonic acid biosynthetic process |
| Acc: |
GO:0019294 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of keto-3-deoxy-D-manno-octulosonic acid, an acidic sugar present in lipopolysaccharides of the outer membranes of some Gram-negative bacteria. |
Synonyms:
- keto-3-deoxy-D-manno-octulosonic acid synthesis
- keto-3-deoxy-D-manno-octulosonic acid biosynthesis
- keto-3-deoxy-D-manno-octulosonic acid anabolism
- KDO biosynthesis
- KDO biosynthetic process
- keto-3-deoxy-D-manno-octulosonic acid formation
- ketodeoxyoctanoate biosynthetic process
|