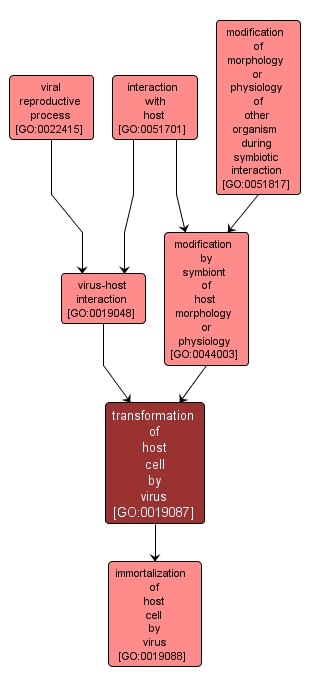
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
transformation of host cell by virus |
| Acc: |
GO:0019087 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
Any virus-induced change in the morphological, biochemical, or growth parameters of a cell. |
Synonyms:
- viral transformation
- viral transformation of host cell
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|