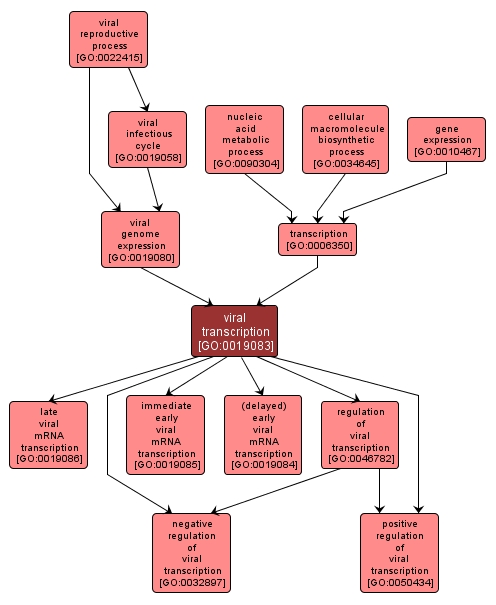
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
viral transcription |
| Acc: |
GO:0019083 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
The mechanisms involved in viral gene transcription, especially referring to those with temporal properties unique to viral transcription. |
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|