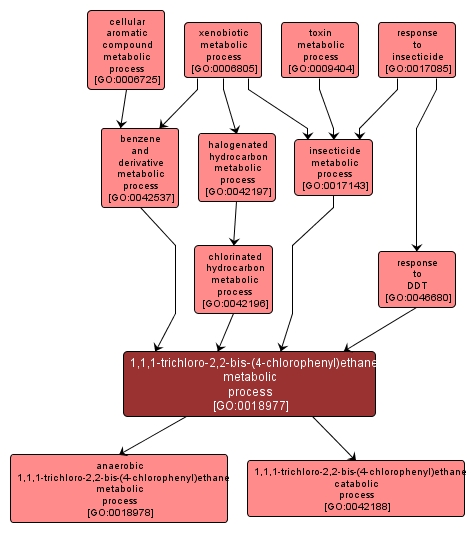
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
1,1,1-trichloro-2,2-bis-(4-chlorophenyl)ethane metabolic process |
| Acc: |
GO:0018977 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
The chemical reactions and pathways involving 1,1,1-trichloro-2,2-bis-(4-chlorophenyl)ethane (DDT), a chlorinated broad spectrum contact insecticide. |
Synonyms:
- 1,1,1-trichloro-2,2-bis-(4-chlorophenyl)ethane metabolism
- DDT metabolic process
- DDT metabolism
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|