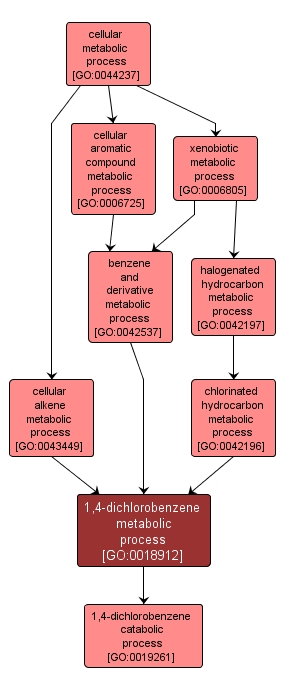
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
1,4-dichlorobenzene metabolic process |
| Acc: |
GO:0018912 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
The chemical reactions and pathways involving 1,4-dichlorobenzene (p-dichlorobenzene or paramoth), a derivative of benzene with two chlorine atoms attached at opposite positions on the ring. It forms white crystals at room temperature and is used as an insecticidal fumigant, particularly in mothballs. |
Synonyms:
- 1,4-dichlorobenzene metabolism
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|