GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
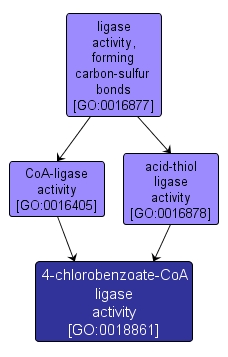
4-chlorobenzoate-CoA ligase activity |
| Acc: |
GO:0018861 |
| Aspect: |
Molecular Function |
| Desc: |
Catalysis of the reaction: 4-chlorobenzoate + CoA + ATP = 4-chlorobenzoyl-CoA + AMP + diphosphate. Requires magnesium and is part of the bacterial 2,4-dichlorobenzoate degradation pathway. |
Synonyms:
- 4-chlorobenzoate:CoA ligase activity
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|