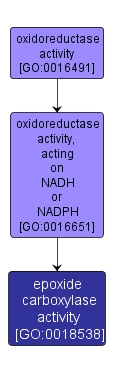
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
epoxide carboxylase activity |
| Acc: |
GO:0018538 |
| Aspect: |
Molecular Function |
| Desc: |
Catalysis of the reaction: ring opening and carboxylation of an epoxide; the reaction requires CO2 as a cosubstrate and forms a beta-keto acid as a products. An example of such a reaction is: epoxypropane + CO2 + NAD+ + NADPH = acetoacetate + NADH + NADP+. |
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|